-
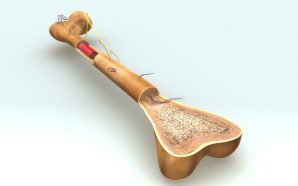
Multiple Myeloma is a cancer which develops in the plasma cells of bone marrow. Plasma cells are a type of white blood cell responsible for the production of antibodies which target and attack germs found within the body. However, when cancer develops inside of a plasma cell, the cell...
-
Eczema is a broad term which refers to a group of skin conditions that can affect all age groups. Generally, eczema is a chronic (long-lasting) inflammatory condition causing dry, red patches of skin which can often be very itchy. Severity can be mild to severe with eczema affecting large or...
-
Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer which forms on the inside of a plasma cell. Plasma cells are a type of white blood cell which helps defend the body against germs. These cells can be found inside the bone marrow; a soft substance inside bones which contains blood....
-
In medical and cancer terminology, a relapse (or recurrence) refers to the return of a disease after a period in which the disease seemed to be going away (remission). A relapse can occur at any stage of cancer remission. In some cases, a certain therapy may be shrinking a...
-
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is a skin rash that often causes pain around the infected area. It is typically characterized by unpleasant red blotches on the skin, somewhat similar to chicken pox but usually only limited to one specific area of the body. Other symptoms of shingles...
-
Shingles is often a painful skin condition. It takes the form of a skin rash, characterized by red blotches on the skin. In some ways, it is similar to chickenpox, except shingles tends to occur in localized areas rather than on the entire body. In addition to a skin...
-
AFib—known medically as Atrial Fibrillation—is a condition that affects the heart, causing it to beat irregularly. More specifically, the upper chambers of the heart will ‘quiver’ instead of pumping effectively. This is caused by the abnormal firing of electrical impulses. Although not always the case, people suffering from AFib...
-
Pulmonary Fibrosis (PF) is a disease which occurs when lung tissue is damaged or scarred. This causes the tissue in the lungs to become thick or stiff. It is, therefore, more difficult for the oxygen inhaled into your lungs to be absorbed into the blood. This can result in...
-
Pulmonary fibrosis can be tough to live with. It is a disease that affects the way you breathe, which may make it feel difficult to manage. The disease is typified by damaged or scarred lung tissue, which then hardens or becomes stiff. This means that it is harder for oxygen...
-
Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted disease (STD). It is thought that over 1 in 6 people between the ages of 14 and 49 have the disease in the United States. It is caused by two types of virus: Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and herpes simplex...
-
is a prescription oral drug typically used to treat high blood pressure. It is also being investigated for use in treating AFib – also known as Atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation is a heart condition that is characterized by an irregular heartbeat. This occurs when the upper chambers of the...
-
Herpes is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). In fact, according to Medical News Today, it is thought that over half of the United States population has herpes type-1—also known as oral herpes—while around 15.5% have herpes type-2—also known as genital herpes. As such, people should...
-
Pulmonary Fibrosis (PF) is a lung disease which presents many problems to patients. Due to the scarring and stiffening of lung tissue associated with PF, patients may find that the disease is affecting the way they breathe. This is because the damaged lung tissue makes it harder for inhaled...
-
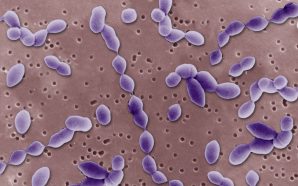
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a type of bacteria responsible for causing pneumococcal disease. Infections by this type of bacteria result in a number of illnesses including pneumonia, meningitis, ear and sinus infections and bacteremia. The bacteria is typically spread via close contact with an infected person as well as through...
-
Hepatitis C (Hep C) is a viral infection of the liver. It spreads from person to person in a variety of ways, but always through blood or other bodily fluids. This means that it is possible to catch Hepatitis C from infected needles and unprotected sex. It can also...
-
Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer which forms inside of blood plasma cells. These cells are normally responsible for helping the body fight off infection by producing antibodies. Antibodies will track down and destroy any foreign bacteria which find their way into the blood, preventing illness. However,...
-
Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer which is formed by malignant blood plasma cells. These cells are responsible for producing the antibodies which make up the body’s defense arsenal in the immune system. These plasma cells are found in the fleshy center of bones – the bone...
-
Multiple Myeloma is a type of cancer which can be found in the plasma cells of bone marrow. These cells are responsible for producing antibodies which help the body fight infection. However, when a plasma cell begins to behave abnormally and undergoes a change, it may begin to...
-
Multiple Myeloma is a type of cancer that affects plasma cells. These cells are present in bone marrow – the soft tissue which is found on the inside of bones. When the plasma cells become infected, they begin to duplicate aggressively, forming a tumor which can damage bones...
-
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease which affects the skin, characterized by red, scaly rashes across affected areas. The most common type of psoriasis is plaque psoriasis, which causes red, raised patches of skin covered with silvery scales. These plaque patches may be itchy and painful, and the severity can...
-
Tooth pain can be annoyingly painful, particularly if you know you have to wait a while for your dentist appointment. So what can you do until then? There are a few home remedies you can use to minimize discomfort, but if you’d rather go over-the-counter, then Orajel is a...
-
An abscess occurs when the pulp chamber inside a tooth becomes infected. The pulp chamber is a collection of nerves and blood vessels which runs up through the inside of the tooth. The infection then spreads and multiplies down through the tooth, before collecting down at the tooth root...
-
Tooth pain can result from a number of conditions inside the mouth. A broken or decayed tooth, food caught between teeth, wisdom tooth pain and gum ulcers can all cause mild-to-severe pain. This pain can interrupt day-to-day activities such as sleep, work, and eating, and can be all-the-more annoying...
-
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs, resulting in lung inflammation. The infection is usually bacterial or viral. The severity of the condition varies widely but generally, symptoms include coughing up mucus, a fever, chest pain, weakness, shortness of breath, nausea and diarrhea. These symptoms are generally more severe...
-
‘Pneumococcal’ is a broad term. Generally, it is characterized by any condition caused by the pneumococcus bacteria. This bacteria can cause a host of infections, including ear infections, sinus infections, meningitis, and bacteremia. One of the most common pneumococcal conditions is pneumonia – infection of the lungs. Pneumococcal pneumonia...
-
Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints in the US. It is typically defined as when a person has fewer than 3 bowel movements per week, or who also suffers from hard stools and incomplete bowel movements. A survey by the American Gastroenterological Association showed that around...
-
The pneumonia shot (injection) is one of the leading methods of preventing the spread of pneumonia. It is also known as the pneumonia vaccine or pneumococcal vaccination, and it comes in two types. Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV13 / 13) PCV13 protects against 13 different types of pneumonia bacteria. PCV13...
-
Hemophilia is a medical condition which occurs when the body does not produce enough clotting factor in the blood. This means that the blood is unable to clot, which causes excessive bleeding, either inside or outside the body. There are two types of clotting factor that may be missing...