Pulmonary embolism is a serious, potentially life-threatening medical emergency in which a blood clot blocks an artery that brings blood to one or both lungs. Since blood flow to the lungs is the only way oxygen can enter the bloodstream, pulmonary embolism requires treatment as soon as possible.
The final outcome of the condition varies from patient to patient: Some make full recoveries, while others require continued treatment and a lengthy hospital stay, and a smaller percentage will die soon after onset. Whether or not someone recovers often depends on how quickly he or she receives treatment, so seek immediate medical care if you develop one or more of the following symptoms.
Shortness of Breath
One of the most common symptoms of pulmonary embolism is dyspnea or shortness of breath. This symptom may be similar to the feeling after intense exercise, but the onset is rapid and does not improve with rest. It is often frightening, as patients experiencing this will not be able to catch their breath no matter what they do. Typically, this symptom worsens upon exertion–for example, walking can become exhausting or painful.
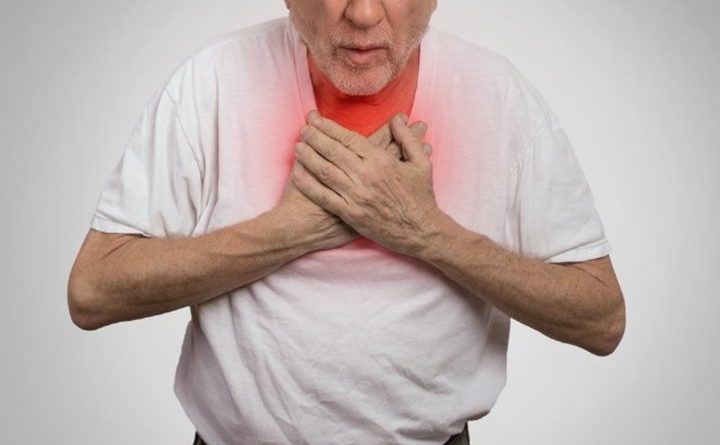
Chest Pain
Most patients with pulmonary embolism experience chest pain. Often, the pain is sharp and stabbing and occurs on one side, though it may also feel like a burning, aching, or heavy sensation that radiates through one or both shoulders. The severity of this pain can cause a patient to bend over and hold his or her chest.
One of the key features of chest pain associated with this condition is that it usually gets much worse during deep breathing; this can compound the shortness of breath.
Sudden Coughing
Patients diagnosed with pulmonary embolism often report waking up with a cough that doesn’t go away. This is accompanied by a persistent feeling of something being “stuck.” In severe cases, coughing up blood also occurs.
Leg Pain and Swelling
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is the single biggest risk factor for pulmonary embolism. DVT is a condition that involves the formation of a blood clot in a vein in the leg. The clot can break free and travel to the lungs, causing pulmonary embolism. Swelling, redness, numbness or pain in one leg–symptoms of DVT–might be the only sign of pulmonary embolism.
Other Symptoms
Less common symptoms associated with pulmonary embolism include sweating, bluish skin, rapid heart rate, dizziness, fainting, and wheezing. These arise as the body responds to a lack of adequate oxygen.
Medical Attention
If you have any of the symptoms discussed above, immediately make your way to the nearest hospital. Emergency physicians will run specific tests and decide on proper treatment.
If you have had a recent heart attack or stroke, had surgery in the past month, taken birth control pills or estrogen, or have been diagnosed with pulmonary embolism or deep vein thrombosis, you are at greater risk for pulmonary embolism.
Featured Image: twitter